B
Bravo Charlie
Guest

The 'Football War' was fought by Central American countries El Salvador and Honduras in 1969. Both were mostly equipped with out-dated WWII era American weaponry. This war also went by the name of the '100 Hours' War', and in reality there were a host of issues at the root of the troubles. Migration, trade and simmering land disputes on the border all conspired to spark social unrest between the two, but it wasn't until the best-of-three World Cup qualifiers in 1969 that the tipping point was reached.
The first game - a 1-0 win for Honduras - in Tegucigalpa witnessed disturbances but things deteriorated significantly come the second in San Salvador: visiting Honduran players, according to Ryszard Kapuściński's 1978 book Wojna Futbolowa, endured a sleepless night before the game, with rotten eggs, dead rats and stinking rags all tossed through the broken windows of their hotel; Honduran fans were brutalised at the game, and the country's flag and national anthem were also mocked. "Under such conditions the players from Tegucigalpa did not, understandably, have their minds on the game," admitted the Honduras coach Mario Griffin after his team lost 3-0. "They had their minds on getting out alive. We're awfully lucky that we lost."

Tension continued to increase before the decisive third match in Mexico, with the press stoking the frenzy. And on June 27 - the day of the play-off - Honduras broke off diplomatic relations with their neighbour. El Salvador eventually triumphed 3-2 after extra-time, booking their place in the 1970 World Cup (where they would lose all three of their group games without scoring). By July 14, El Salvador had invaded Honduras.

Early on the morning of July 14, 1969, concerted military action began. The Salvadoran air force attacked targets inside Honduras and the Salvadoran army launched major offensives along the main road connecting the two nations and against the Honduran islands in the Golfo de Fonseca. At first, the Salvadorans made fairly rapid progress.
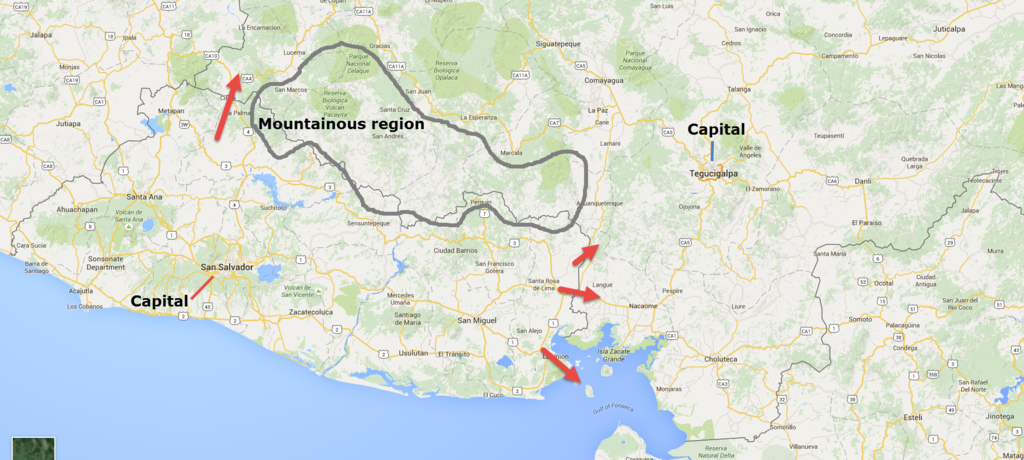
By the evening of July 15, the Salvadoran army, which was considerably larger and better equipped than its Honduran opponent, pushed the Honduran army back over eight kilometers and captured the departmental capital of Nueva Ocotepeque.

Thereafter, the attack bogged down, and the Salvadorans began to experience fuel and ammunition shortages. A major reason for the fuel shortage was the action of the Honduran air force, which--in addition to largely destroying the smaller Salvadoran air force--had severely damaged El Salvador's oil storage facilities.

The day after the fighting had begun, the OAS met in an urgent session and called for an immediate cease-fire and a withdrawal of El Salvador's forces from Honduras. El Salvador resisted the pressures from the OAS for several days, demanding that Honduras first agree to pay reparations for the attacks on Salvadoran citizens and guarantee the safety of those Salvadorans remaining in Honduras. A cease-fire was arranged on the night of July 18; it took full effect only on July 20. El Salvador continued until July 29 to resist pressures to withdraw its troops. Then a combination of pressures led El Salvador to agree to a withdrawal in the first days of August 1969.
The 'Football War' could someday be used to form the back-drop for a fictional CM Campaign along the lines of the concept developed by Rico in his fictional island campaign...
Last edited by a moderator:


































































































